Exploring the intricate relationship between interest rates and the stock market reveals a fascinating interplay that shapes investment decisions and market trends. Dive into this compelling narrative to uncover the profound effects of interest rates on stock prices and investor strategies.
As we delve into the key factors influencing stock market reactivity to interest rates and analyze the impact of interest rate changes on various sectors, you'll gain valuable insights into navigating the dynamic terrain of the stock market.
Overview of Interest Rates and Stock Market Relationship
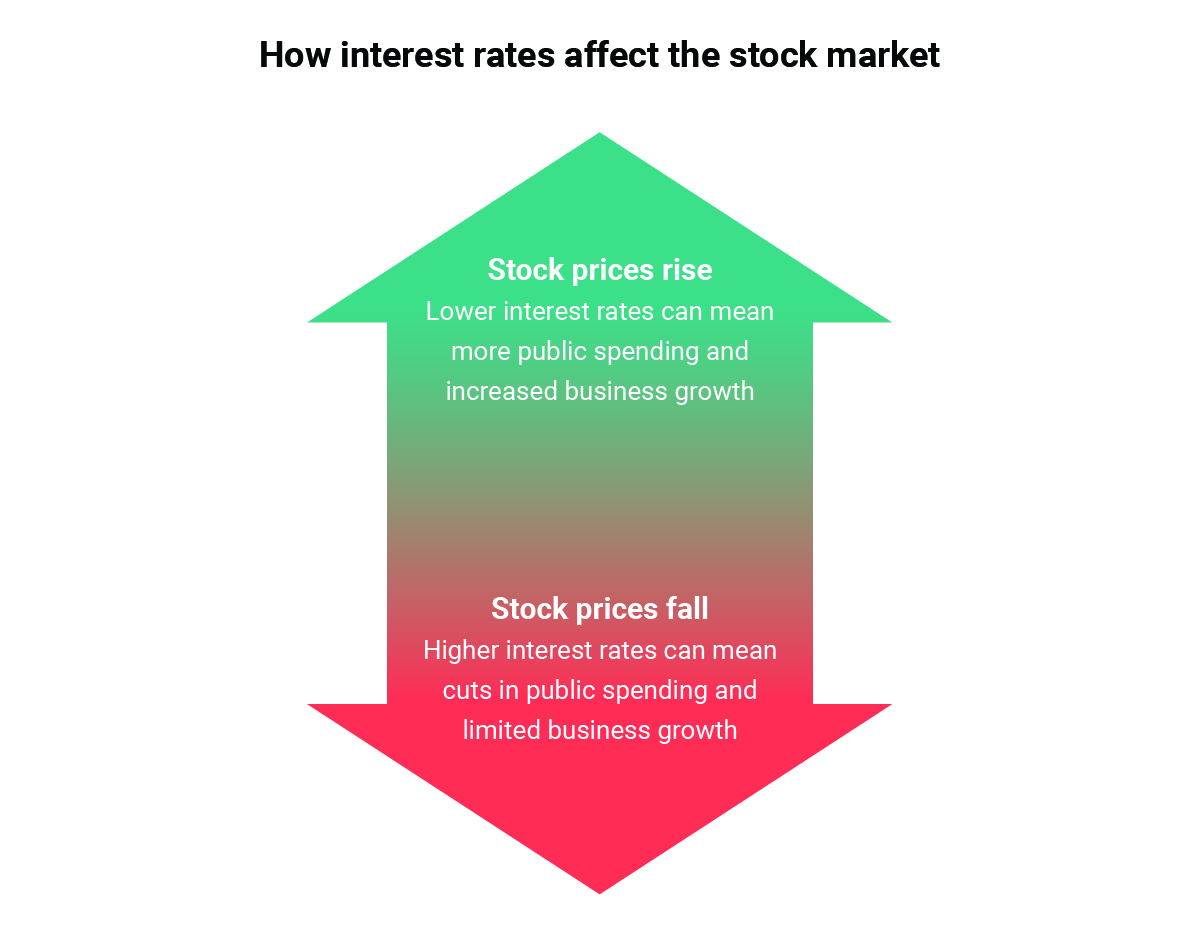
Interest rates play a crucial role in the functioning of the economy and have a direct impact on various financial instruments, including the stock market. When the central bank adjusts interest rates, it affects borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall economic activity.
This, in turn, influences stock prices and investor behavior.
Impact of Interest Rates on the Stock Market
Interest rates have a significant influence on the stock market in several ways. Here are some key points to consider:
- Interest Rates and Stock Valuations: Lower interest rates generally lead to higher stock valuations as companies can borrow money at a lower cost, increasing their profitability and growth potential.
- Interest Rates and Investor Behavior: Higher interest rates may make bonds and other fixed-income investments more attractive compared to stocks, leading investors to shift their portfolio allocations, impacting stock prices.
- Interest Rates and Economic Growth: Changes in interest rates can signal shifts in the overall economy. For example, a decrease in interest rates may indicate efforts to stimulate economic growth, which can positively impact stock prices.
It's essential for investors to monitor changes in interest rates as they can provide valuable insights into market trends and potential investment opportunities.
Historical Trends
Looking back at historical data, we can observe how interest rate changes have influenced the stock market. For instance, during periods of economic expansion, rising interest rates have sometimes led to market corrections as investors anticipate the impact on corporate earnings and borrowing costs.
Conversely, during economic downturns, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate growth, which can boost stock prices.
- In the early 1980s, when the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to combat inflation, the stock market experienced a significant downturn.
- Following the 2008 financial crisis, central banks globally implemented low-interest rate policies to spur economic recovery, contributing to a prolonged bull market in stocks.
Factors Influencing Stock Market Reactivity to Interest Rates

Interest rates have a significant impact on the stock market, influencing investors' decisions and overall market performance. Several key factors determine how the stock market responds to changes in interest rates, including inflation rates, economic growth projections, and sector-specific dynamics.
Role of Inflation
Inflation plays a crucial role in the relationship between interest rates and the stock market. When inflation is high, central banks may increase interest rates to curb rising prices. This can lead to higher borrowing costs for businesses, potentially impacting their profitability and stock prices.
Conversely, lower inflation rates may result in lower interest rates, stimulating economic growth and boosting stock market performance.
Sector Reactions to Interest Rate Changes
Different sectors of the stock market may react differently to changes in interest rates. For example:
- Interest-sensitive sectors such as real estate and utilities tend to be negatively impacted by rising interest rates, as higher borrowing costs can reduce demand for their products and services.
- Conversely, sectors like financials may benefit from higher interest rates, as they can earn more on their investments and loans.
- Technology and growth stocks, on the other hand, may be more sensitive to interest rate changes due to their reliance on future earnings and cash flow expectations.
- Defensive sectors like healthcare and consumer staples may exhibit more stable performance during interest rate fluctuations, as their products and services are considered essential regardless of economic conditions.
Overall, understanding these sector-specific reactions can help investors make informed decisions based on interest rate trends and their potential impact on the stock market.
Impact of Interest Rate Hikes on Stock Prices
When interest rates are increased by the central bank, it can have a significant impact on stock prices. Investors tend to react to these changes as they assess the implications for various industries and companies in the stock market.
Stock Price Reaction to Interest Rate Hikes
- Stock prices typically decrease when interest rates are hiked. This is because higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs for companies, leading to lower profits and potentially reducing the attractiveness of stocks as an investment.
- Investors may also shift their focus towards fixed-income securities like bonds, which become more appealing with higher interest rates, causing a decrease in demand for stocks.
Industries Affected by Interest Rate Hikes
- Interest rate hikes can impact industries differently based on their sensitivity to borrowing costs and economic conditions. For example, sectors like real estate and construction may be more affected as higher mortgage rates can reduce demand for homes and construction projects.
- On the other hand, industries like utilities and consumer staples, which are known for stable earnings and dividends, may be less impacted by interest rate hikes due to their defensive nature.
Investor Strategies During Rising Interest Rates
- During periods of rising interest rates, investors may consider diversifying their portfolios to include assets that are less sensitive to interest rate fluctuations, such as dividend-paying stocks with strong fundamentals.
- Additionally, investors can focus on companies with solid balance sheets and low debt levels, which may be better positioned to weather the impact of higher interest rates on their operations.
Effect of Lowering Interest Rates on Stock Market Performance
Lowering interest rates can have a significant impact on stock market performance. When interest rates are decreased by central banks, borrowing becomes cheaper, leading to increased spending and investment by businesses and consumers. This influx of capital can stimulate economic growth, which in turn can boost corporate profits and stock prices.
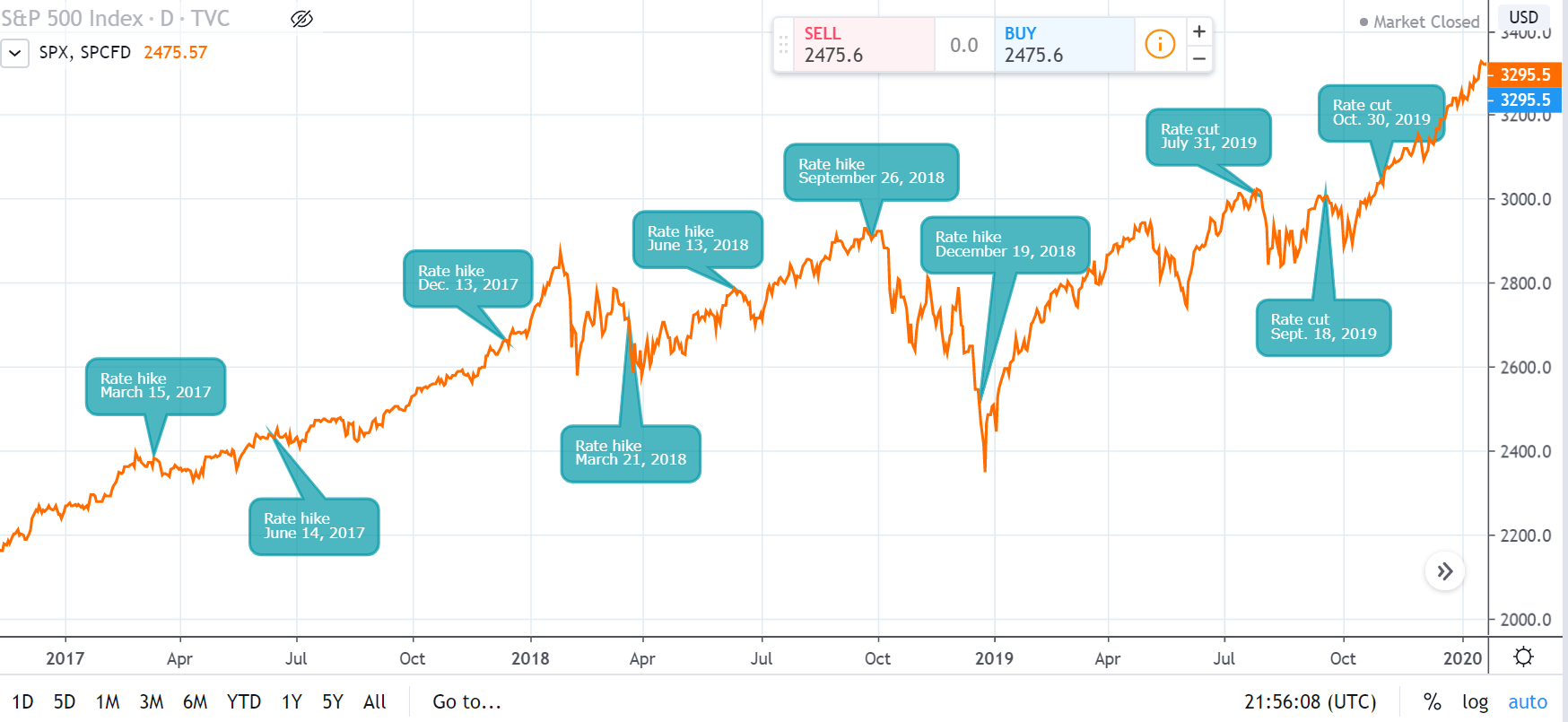
Historical Data Analysis of Stock Market Response to Interest Rate Cuts
One notable example of the stock market's response to interest rate cuts is the period following the 2008 financial crisis. The Federal Reserve drastically lowered interest rates to near-zero levels to stimulate the economy. This move was accompanied by a strong rally in the stock market, with major indices posting significant gains over the subsequent years.
- During the period of rate cuts, the S&P 500 index surged by over 200% from its lows in 2009.
- Technology and financial sectors, in particular, benefited greatly from the low-interest-rate environment, leading to substantial gains for investors.
- Lower interest rates also tend to make bonds less attractive compared to stocks, driving investors towards equities and further boosting stock prices.
It is essential to note that the stock market's response to interest rate cuts may vary depending on the overall economic conditions and market sentiment at the time.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Low-Interest-Rate Environment for Investors
A low-interest-rate environment can offer several benefits for investors, including easier access to credit, lower borrowing costs, and higher asset prices. However, there are also drawbacks to consider.
- Benefits:
- Increased investment activity and consumer spending can drive economic growth, benefiting companies and boosting stock prices.
- Lower borrowing costs can improve profit margins for businesses, leading to higher earnings and potentially higher stock valuations.
- Investors seeking yield may turn to stocks as bond yields decline, further supporting equity markets.
- Drawbacks:
- Low-interest rates can lead to asset bubbles as investors chase higher returns, potentially resulting in market volatility and increased risk.
- Savers and retirees relying on fixed-income investments may face challenges in generating sufficient income in a low-rate environment.
- Central banks may struggle to raise rates in the future if needed, limiting their ability to combat inflation or economic downturns.
Last Word
In conclusion, understanding how interest rates impact the stock market is crucial for investors looking to make informed decisions. By recognizing the implications of interest rate hikes and cuts on stock prices, investors can adapt their strategies to capitalize on market opportunities.
Stay informed, stay strategic, and navigate the stock market with confidence.
Helpful Answers
How do interest rates affect stock market performance?
Interest rates impact stock market performance by influencing borrowing costs, company earnings, and investor sentiment.
Are certain sectors more sensitive to interest rate changes?
Yes, sectors such as banking, real estate, and utilities are typically more sensitive to interest rate changes compared to others.
What strategies can investors use during periods of rising interest rates?
Investors can consider diversifying their portfolios, focusing on defensive stocks, and monitoring interest rate trends closely.
How does inflation play a role in the relationship between interest rates and the stock market?
Inflation influences interest rate decisions by central banks, which in turn affect stock market performance and investor behavior.